About Lipedema
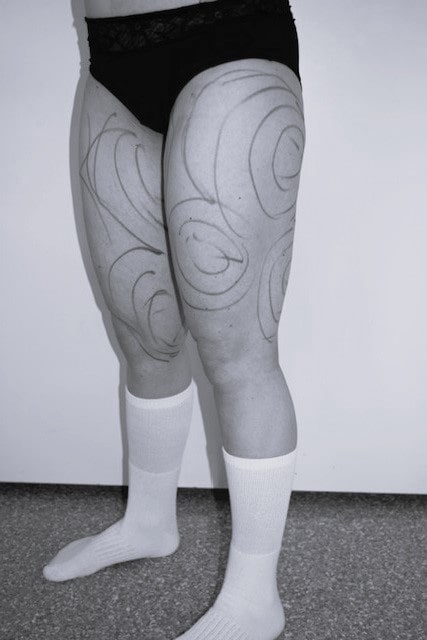
Lipedema is a chronic condition primarily affecting women, characterized by abnormal fat accumulation in symmetrical patterns, often in the legs, hips, and buttocks. In some cases, the arms are also affected, but the hands and feet usually remain unaffected. Symptoms include swelling, easy bruising in the impacted areas, tenderness, and pain. The chronic disease is resistant to conventional weight loss methods, allowing weight loss in the upper body while the affected areas remain unchanged. This condition can lead to decreased quality of life over time due to pain, mobility challenges, and psychological distress.
What causes lipedema?
The exact cause of lipedema is unknown, but it is often associated with hormonal changes and genetic factors. It can be easily mistaken for other conditions such as lymphedema or obesity. Individuals with lipedema can maintain a healthy weight despite the condition. Due to these knowledge gaps and common misconceptions, there is a critical need for increased awareness and research to better understand and support those affected by lipedema.
Symptoms
- Pain, discomfort or tenderness in affected areas.
- Enlargement of legs/arms (but usually not your feet or hands).
- Legs with dimples and a bumpy texture.
- Spider veins or varicose veins on your legs.
- Difficulty walking because of changes in your leg shape, heavy legs, or flat-feet.
- Swelling (often worse in the afternoon, evening, after activity or in hot weather).
- Easy bruising in affected areas.
Types of lipedema
There are four different types, depending on the location of fat build up and resulting body shape (Lipedema Foundation, n,d.) For more information please visit Lipedema Foundation.
How can you treat this?
- Physical Therapy
- Exercise
- Nutrition
- Emotional Support
- Compression Therapy
- Surgery
Physical Therapy
Recent studies indicate that physical therapy can significantly reduce inflammation and pain associated with lipedema.
Exercise
Staying active helps stimulate the lymphatic system, supports joint health, and builds strength. Activities such as swimming, biking, cycling, Pilates, yoga, and walking can help reduce swelling and improve mobility.
Nutrition
While lipedema fat doesn’t respond to calorie reduction, you can ease symptoms and reduce fat build-up by monitoring your diet. Consuming anti-inflammatory foods can be beneficial. Since dietary needs vary, keeping track of which foods improve or worsen your symptoms can be helpful.
Emotional Support
Receiving professional guidance and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are crucial for effectively managing lipedema.
Compression Therapy
Compression garments can alleviate inflammation, pain, and swelling. Available in various types, sizes, and strengths, they can enhance both body composition and quality of life.
Surgery
Procedures such as liposuction, vein surgery, and joint replacements can help reduce pain and improve mobility. However, surgery is not a quick fix; it requires careful consideration and adherence to pre- and post-operative instructions.
Sources
- www.lipedema.org and my.clevelandclinic.org
- www.lipdedema.org
- Accessed: 23.05.2024
